Click on image to view larger version.

Fig. 2. Microfibril and elastic fibre formation. Fibrillin is assembled
pericellularly into microfibrillar arrays that appear to undergo
time-dependent maturation into beaded transglutaminase-crosslinked
microfibrils. Mature microfibrils form parallel bundles that may be stabilised
at inter-microfibrillar crosslinked regions. In elastic tissues, tropoelastin
is deposited on microfibril bundles, and lysyl oxidase-derived crosslinks then
stabilise the elastin core. Crosslinks catalysed by the actions of
transglutaminase and lysyl oxidase are shown. Transglutaminase forms
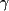 -glutamyl-e-lysine isopeptide bonds within or between peptide chains.
Lysyl oxidase catalyses the oxidative deamination of certain lysine residues
in elastin and subsequent, probably spontaneous, reactions lead to the
formation of bifunctional crosslinks (dehydrolysinonorleucine and allysine
aldol), a trifunctional crosslink (dehydromerodesmosine), and two
tetrafunctional crosslinks (desmosine and isodesmosine, shown here).
-glutamyl-e-lysine isopeptide bonds within or between peptide chains.
Lysyl oxidase catalyses the oxidative deamination of certain lysine residues
in elastin and subsequent, probably spontaneous, reactions lead to the
formation of bifunctional crosslinks (dehydrolysinonorleucine and allysine
aldol), a trifunctional crosslink (dehydromerodesmosine), and two
tetrafunctional crosslinks (desmosine and isodesmosine, shown here).
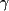 -glutamyl-e-lysine isopeptide bonds within or between peptide chains.
Lysyl oxidase catalyses the oxidative deamination of certain lysine residues
in elastin and subsequent, probably spontaneous, reactions lead to the
formation of bifunctional crosslinks (dehydrolysinonorleucine and allysine
aldol), a trifunctional crosslink (dehydromerodesmosine), and two
tetrafunctional crosslinks (desmosine and isodesmosine, shown here).
-glutamyl-e-lysine isopeptide bonds within or between peptide chains.
Lysyl oxidase catalyses the oxidative deamination of certain lysine residues
in elastin and subsequent, probably spontaneous, reactions lead to the
formation of bifunctional crosslinks (dehydrolysinonorleucine and allysine
aldol), a trifunctional crosslink (dehydromerodesmosine), and two
tetrafunctional crosslinks (desmosine and isodesmosine, shown here).