 |
EVOLUTION 101
Introduction
Patterns
Mechanisms
Microevolution
Speciation
Macroevolution
The big issues
 |  |  |
|
The causes of mutations
Mutations happen for several reasons.
- DNA fails to copy accurately
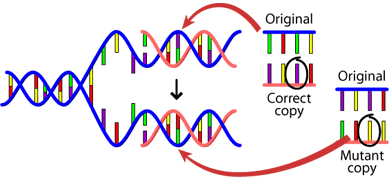
Most of the mutations that we think matter to
evolution are "naturally-occurring." For example, when a cell divides, it makes a
copy of its DNA — and sometimes the copy is not quite perfect. That small
difference from the original DNA sequence is a mutation.

To download this image, right-click (Windows) or control-click (Mac) on the image and select "Save image."
|
External influences can create mutations
 Mutations can also be caused
by exposure to specific chemicals or
radiation. These agents cause the DNA to break down. This is not necessarily
unnatural — even in the most isolated and pristine environments, DNA breaks
down. Nevertheless, when the cell repairs the DNA, it might not do a perfect job
of the repair. So the cell would end up with DNA slightly different than the
original DNA and hence, a mutation. Mutations can also be caused
by exposure to specific chemicals or
radiation. These agents cause the DNA to break down. This is not necessarily
unnatural — even in the most isolated and pristine environments, DNA breaks
down. Nevertheless, when the cell repairs the DNA, it might not do a perfect job
of the repair. So the cell would end up with DNA slightly different than the
original DNA and hence, a mutation.
|
 |
 |
 |
Mechanisms
page 7 of 22


| Learn more about mutation in context:
|

 |


